Cytokines-mediated signaling is a primary way of immune system communication.
The common gamma-chain family of cytokines is a set of six cytokines that signal through the common cytokine γ chain receptor (γc/CD132/IL2RG). These cytokines include IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21. Besides the IL-2RG receptor subunit, the γc family cytokine receptors include IL-2RB (CD122), IL-4R (CD124), IL-7R (CD127), IL-9R (CD129), and IL-21R (Fig. 1). These cytokines activate three major signaling pathways (PI3K-Akt, RAS-MAPK, and JAK-STAT), regulating the development, survival, proliferation, differentiation, and function of immune cells, especially, T-lymphocytes. Targeting or using these cytokines as therapeutic agents has shown potential in allergy, immunodeficiency, autoimmunity, and cancer immunotherapy.
The pathways, specificity, and activation patterns associated with gamma chain cytokines
Each member of the cytokine family is capable of activating both JAK1 and JAK3. In fact, JAK1 directly interacts with IL-2Rb, IL-4Ra, IL-7Ra, IL-9Ra, and IL-21Ra. JAK3, on the other hand, interacts with the gamma chain. However, when it comes to the STAT proteins, IL-2, IL-7, IL-9, and IL-15 modulate the activation of STAT5A and STAT5B. IL-4 is associated with the activation of STAT6, and IL-21 activates STAT3. The specificity of the signaling cascades mediated by these cytokines is dictated by the activation stimuli and action cell type. Besides JAK-STAT, the other signaling pathways that gamma chain cytokines can activate include MAPK (IL-2), PI3K pathway (IL-2, IL-7), and the phosphorylation of the adaptor molecule IRS2, which links the downstream signaling pathways (IL-4). Gamma chain cytokines, however, are not just restricted to immune cells. For instance, IL-2R subunits, in addition to JAK3, are also expressed on endothelial cells.
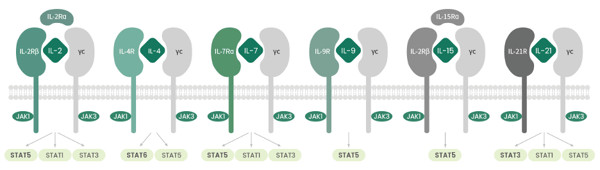
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the gamma chain cytokines and their receptors
Recent advances in the roles of common gamma chain cytokines in cancer immunotherapy:
Cytokines are complex immunomodulators. The function of cytokines in cancer immunity can be spatiotemporally specific. Some common gamma chain cytokines promote tumor growth, proliferation, and differentiation, while others mediate antitumor responses. Cytokine therapy is a promising avenue for cancer immunotherapy where cytokine modulation can directly impact tumors or be employed as adjuvant therapy.
IL-2
The IL-2 common gamma chain cytokine has the heterotrimeric receptor formed by IL-2Rb, IL-2Ra, and IL-2RG. IL-2 cytokine therapy has a promising aspect as it mediates antigen-induced cell death, enhances the production of immunoglobulins by B cells, and stimulates the differentiation of T helper (Th) cells into CD8+ T-cells. It also promotes the expression of IL-2 receptor (CD25) while decreasing the surface expression of PD-1, collectively targeting the cancer cells. However, IL-2 also drives the expansion and development of regulatory T cells, suppressing the antitumor immune response. Hence, the IL-2 cytokine therapy pairing with Treg inhibitors has a more robust response in antitumor activity. Currently, IL-2 immunotherapy is used to stimulate the expansion of T-cells as a combination therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors like ipilimumab and nivolumab in melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, and ovarian and colorectal cancers.
IL-4
Unlike IL-2, IL-4 is an immunosuppressive cytokine in the context of cancer immunity. It promotes tumor growth by stimulating the Th2 cell differentiation (pro-tumor), that in turn suppresses the Th1 cells (anti-tumor). IL-4 binding to its receptor, IL-4Ra, generates anti-apoptotic immune responses. In a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy approach, IL-4 inverted receptors are expressed to promote the Th1 phenotypes and promote anti-tumor activity. Drugs like Ruxolitinib and Leflunomide have been tested in clinical trials to block the downstream signaling of IL-4 by inhibiting the Jak-STAT6 activation and the resulting antitumor effects. The antitumor activity of IL-4 inhibition directly by blocking the cytokine-receptor interaction with drugs like Dupilumab, Pitrakinra, and Pascolizumab has been studied in a few clinical trials for different cancers. However, many of these studies have failed to show promising results due to low efficacy, and it continues to be an area of further exploration.
IL-7
IL-7 has been classified as a stromal factor that is inherently essential for the growth and development of T cells. The IL-7 cytokine promotes the proliferation of naïve and memory T cells and is responsible for CD4+ and CD8+ memory T cell homeostasis. It acts independently or synergistically with other family members, IL-2/IL-15 for immunomodulation, especially the expansion of the T cells. Constitutive expression of IL-7 is IL-7 shows a rapid expansion of CAR-T cells, their antitumor activity, and efficacy. The application of IL-7 as an adjuvant with cancer vaccines also shows improvements in antitumor outcomes.
IL-9
IL-9 is generally grouped with IL-4 for its immunosuppressive properties in cancer. However, some studies have implicated the antitumor activity of IL-9, where it can induce inflammation, activate mast cells, and recruit CD8 T cells at the tumor site. The subset of CD4+ T cells, the T helper 9 (Th9) cells, are the central tumor-specific cells that produce IL-9 and are regulated by IL-9 signaling. Mast cell recruitment at the tumor site is associated with a better prognosis. Like IL-7, IL-9 expressing CAR-T cells show enhanced antitumor cytotoxicity with sustained cell proliferation and expansion. Effective adoptive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) therapy is associated with high expression of IL-9, presenting a promising direction for cancer immunotherapy.
IL-15
IL-15 is generally produced by macrophages, monocytes, keratinocytes, and dendritic cells. IL-15 is responsible for the differentiation and expansion of T cells, modulation of memory CD8+ T cell homeostasis, and the development of NK cells. Much like IL-2, IL-15 can enhance CD8+ T cell cytolytic activity while augmenting NK cells’ activity. Like some of the other gamma chain cytokines, IL-15 supports CAR-T cell proliferation, expansion, and sustained antitumor activity. A transgenic membrane-bound version of IL-15 is proposed to improve the survival of CAR-T cells in therapy. A few modified CAR-T cells with IL-15 expression have shown positive results in neuroblastoma, leukemia, and lymphoma.
IL-21
IL-21 is produced by T cells following stimulation via antigen. However, its primarily produced by Th17, NKT, and Follicular helper T cells. IL-21 has also been seen to inhibit the differentiation of regulatory T cells. Although IL-21 activates both Jak1 and Jak3, IL-21Ra primarily interacts with Jak1, while the gamma chain interacts with Jak3. This further activates the STAT proteins, PI3K, and MAPK pathways. IL-21 also synergistically functions with other cytokines to promote T cell differentiation and antitumor effects. As seen for the other gamma chain cytokines, CAR-T cells with constitutive expression of IL-21 show enhanced survival of the cells and antitumor activity. Adoptive CD8 T cells with IL-21 expression also show better expansion of the T cells and tumor-inhibitory responses.
Sino Biological Inc. has developed a panel of high-quality recombinant cytokines and receptors to support the research on the common gamma chain cytokine family (Table 1 and Fig. 2).
Table 1: Selective recombinant proteins for common gamma chain cytokines and receptors
|
Catalog no. |
Cytokine |
Species |
Expression host |
Tag |
|
IL-2 |
Human |
HEK293 |
Native |
|
|
IL-2R alpha |
Human |
HEK293 |
His |
|
|
IL-4 |
Human |
E. coli |
Native |
|
|
IL-4R |
Human |
HEK293 |
AVI and His |
|
|
IL-7 |
Human |
E. coli |
Native |
|
|
IL-7R |
Human |
HEK293 |
hFc |
|
|
IL-9 |
Human |
Baculovirus-Insect cells |
His |
|
|
IL-9R |
Rat |
HEK293 |
His |
|
|
IL-15 |
Human |
E. coli |
Native |
|
|
IL-15R |
Human |
HEK293 |
hFc |
|
|
IL-21 |
Human |
E. coli |
Native |
|
|
IL-21R |
Human |
HEK293 |
His |
|
|
IL2RB |
Human |
HEK293 |
hFc |
|
|
IL2RG |
Human |
HEK293 |
His |
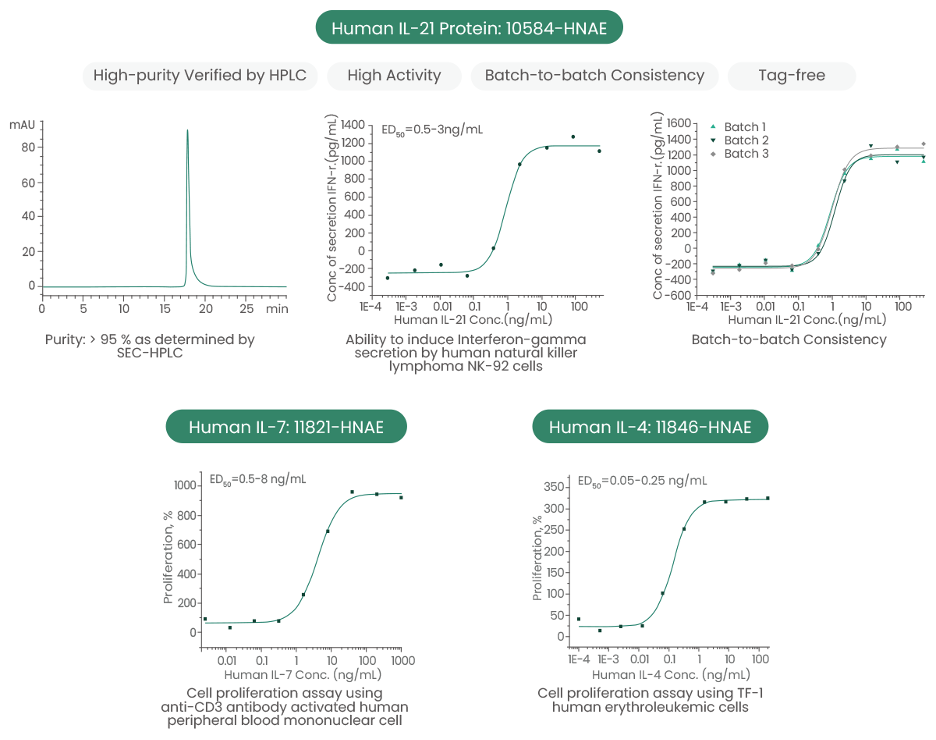
Figure 2: Some optimized and validated featured common gamma chain cytokine recombinant proteins
This discussion is a non-exhaustive list of roles and applications of common gamma chain cytokines in cancer immunotherapy to highlight the potential of modulating these molecules in targeting cancers. New insights into how cytokines attain specificity is bound to shed light on the combinatorial actions of JAKs and STATs while also elucidating how signaling pathways coordinate with each other; for instance, PI3K and ERK-dependent pathways. Such insights will allow the researchers to focus further on human biology, gene regulation, and signaling and invest more attention in a sustainable pharmaceutical operation based on novel therapeutics.
References:
Bell, M., & Gottschalk, S. (2021). Engineered cytokine signaling to improve CAR T cell effector function. Frontiers in Immunology, 12, 684642.
Chulpanova, D. S., Kitaeva, K. V., Green, A. R., Rizvanov, A. A., & Solovyeva, V. V. (2020). Molecular aspects and future perspectives of cytokine-based anti-cancer immunotherapy. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology, 8, 402.
DiToro, D., Winstead, C.J., Pham, D., Witte, S., Andargachew, R., Singer, J.R., Wilson, C.G., Zindl, C.L., Luther, R.J., Silberger, D.J., et al. (2018). Differential IL-2 expression defines the developmental fates of follicular versus non-follicular helper T cells. Science 361, eaao2933.
Hurton, L.V., Singh, H., Najjar, A.M., Switzer, K.C., Mi, T., Maiti, S., Olivares, S., Rabinovich, B., Huls, H., Forget, M.A., et al. (2016). Tethered IL-15 augments antitumor activity and promotes a stem-cell memory subset in tumor-specific T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 113, E7788–E7797.
Kagoya, Y., Tanaka, S., Guo, T., Anczurowski, M., Wang, C.H., Saso, K., Butler, M.O., Minden, M.D., and Hirano, N. (2018). A novel chimeric antigen receptor containing a JAK-STAT signaling domain mediates superior antitumor effects. Nat. Med. 24, 352–359.
Leonard WJ, Lin JX, O'Shea JJ. (2019). The γc Family of Cytokines: Basic Biology to Therapeutic Ramifications, Immunity. 2019 Apr 16;50(4):832-850.
Massoud, A.H., Charbonnier, L.M., Lopez, D., Pellegrini, M., Phipatanakul, W., and Chatila, T.A. (2016). An asthma-associated IL4R variant exacerbates airway inflammation by promoting the conversion of regulatory T cells to TH17-like cells. Nat. Med. 22, 1013–1022.
Qiu, Y., Su, M., Liu, L., Tang, Y., Pan, Y., & Sun, J. (2021). Clinical application of cytokines in cancer immunotherapy. Drug Design, Development, and Therapy, 15, 2269.
Silva, D.A., Yu, S., Ulge, U.Y., Spangler, J.B., Jude, K.M., Laba˜ o-Almeida, C., Ali, L.R., Quijano-Rubio, A., Ruterbusch, M., Leung, I., et al. (2019). De novo design of potent and selective mimics of IL-2 and IL-15. Nature 565, 186–191.
.jpg)